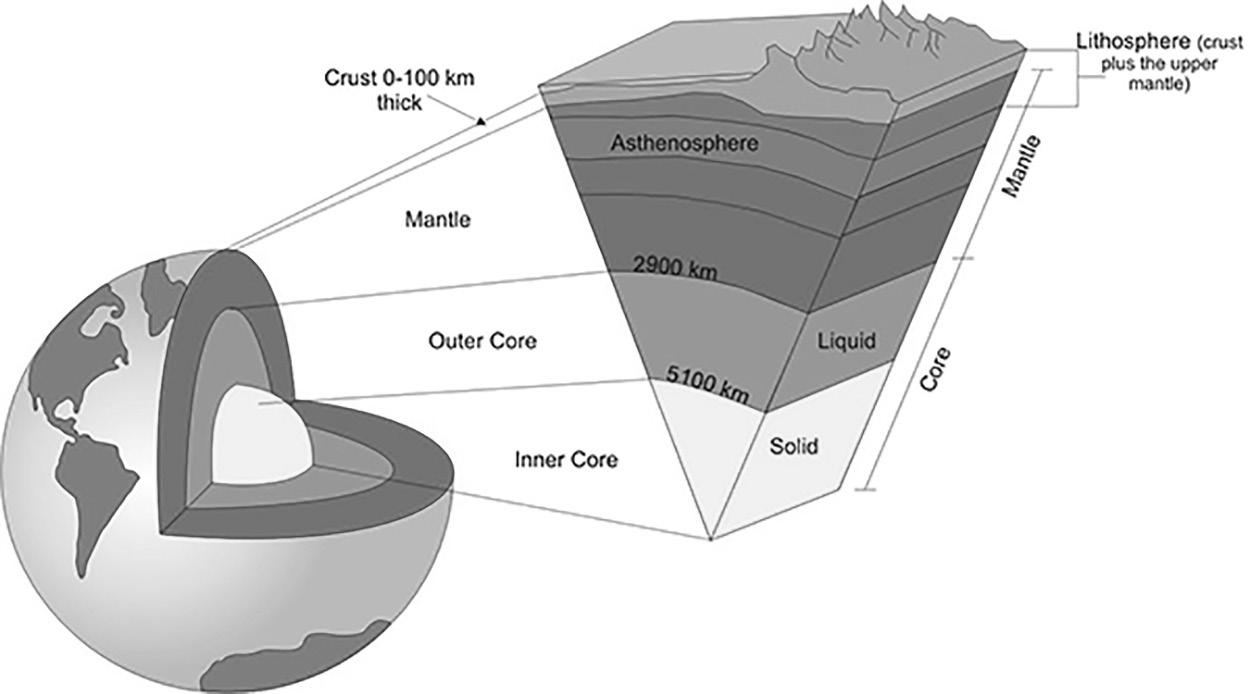
Lithosphere
Continents
There are seven major continents. These are separated by large water bodies.
• These continents are – Asia, Europe, Africa, North America, South America, Australia and Antarctica. The greater part of the land mass lies in the Northern Hemisphere.
Asia
• ASIA is the largest continent. It covers about one third of the total land area of the earth. The continent lies in the Eastern Hemisphere. The Tropic of Cancer passes through this continent. Asia is separated from Europe by the Ural Mountains on the west.
• The combined landmass of Europe and Asia is called the Eurasia (Europe + Asia). EUROPE is much smaller than Asia. The continent lies to the west of Asia. The Arctic Circle passes through it. It is bound by water bodies on three sides.
Africa
• It is the second largest continent after Asia. The Equator or 00 latitude runs almost through the middle of the continent. A large part of Africa lies in the Northern Hemisphere. There is the only continent through which the Tropic of Cancer, the Equator and the Tropic of Capricorn pass. The Sahara Desert, the world’s largest hot desert, is located in Africa.
• The continent is bound on all sides by oceans and seas. World’s longest river the Nile, flows through Africa. Notice where the Equator, the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn pass in the map of Africa.
North America
• It is the third largest continent of the world. It is linked to South America by a very narrow strip of land called the Isthmus of Panama. The continent lies completely in the Northern and Western Hemisphere. Three oceans surround this continent.
South America
• It lies mostly in the Southern Hemisphere. The Andes, world’s longest mountain range, runs through its length from north to south. South America has the world’s largest river, the Amazon.
Australia
• It is the smallest continent that lies entirely in the Southern Hemisphere. It is surrounded on all sides by the oceans and seas. It is called an island continent.
Antarctica
• It completely in the Southern Hemisphere, is a huge continent.
• The South Pole lies almost at the centre of this continent. As it is located in the South Polar Region, it is permanently covered with thick ice sheets. There are no permanent human settlements. Many countries have research stations in Antarctica. India also has research stations there. These are named as Maitri and Dakshin Gangotri.
Hydrosphere
• The earth is called the blue planet. More than 71 per cent of the earth is covered with water and 29 per cent is with land. Hydrosphere consists of water in all its forms.
• As running water in oceans and rivers and in lakes, ice in glaciers, underground water and the water vapour in atmosphere, all comprise the hydrosphere. More than 97% of the Earth’s water is found in the oceans and is too salty for human use.
• A large proportion of the rest of the water is in the form of ice sheets and glaciers or under the ground and a very small percentage is available as fresh water for human use. Hence, despite being a ‘blue planet’ we face a shortage of water. Oceans
• Oceans are the major part of hydrosphere They are all interconnected and are always moving. The three chief movements of ocean waters are the waves, the tides and the ocean currents.
• The five major oceans are the Pacific Ocean, the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, the Southern Ocean and the Arctic Ocean, in order of their size.
• The Pacific Ocean is the largest ocean. It is spread over one-third of the earth. Mariana Trench, the deepest part of the earth, lies in the Pacific Ocean. The Pacific Ocean is almost circular in shape. Asia, Australia North and South Americas surround it.
• The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest Ocean in the world. It is ‘S’ shaped. It is flanked by the North and South Americas on the western side, and Europe and Africa on the eastern side. The coastline of Atlantic Ocean is highly indented. This irregular and indented coastline provides ideal location for natural harbours and ports. From the point of view of commerce, it is the busiest Ocean.
• The Indian Ocean is the only ocean named after a country, that is, India. The shape of ocean is almost triangular. In the north, it is bound by Asia, in the west by Africa and in the east by Australia.
• The Southern Ocean encircles the continent of Antarctica and extends northward to 60 degrees south latitude.
• The Arctic Ocean is located within the Arctic Circle and surrounds the North Pole. It is connected with the Pacific Ocean by a narrow stretch of shallow water known as Berring strait. It is bound by northern coasts of North America and Eurasia.
Atmosphere
• The earth is surrounded by a layer of gas called the atmosphere. This thin blanket of air is an integral and important aspect of the planet. It provides us with the air we breathe and protects us from the harmful effects of sun’s rays. The atmosphere extends up to a height of about 1,600 kilometres. The atmosphere is divided into five layers based on composition, temperature and other properties.
• These layers starting from earth’s surface are called the troposphere, the stratosphere, the mesosphere, the thermosphere and the exosphere.
• The atmosphere is composed mainly of nitrogen and oxygen, which make up about 99 per cent of clean, dry air. Nitrogen 78 per cent, oxygen 21 per cent and other gases like carbon dioxide, argon and others comprise 1 per cent by volume. Oxygen is the breath of life while nitrogen helps in the growth of living organisms.
• Carbon dioxide, though present in minute amount, is important as it absorbs heat radiated by the earth, thereby keeping the planet warm. It is also essential for the growth of plants. The density of the atmosphere varies with height. It is maximum at the sea level and decreases rapidly as we go up. You know, the climbers experience problems in breathing due to this decrease in the density of air.They have to carry with them oxygen cylinders to be able to breathe at high altitudes. The temperature also decreases as we go upwards. The atmosphere exerts pressure on the earth.
This varies from place to place. Some areas experience high pressure and some areas low pressure. Air moves from high pressure to low pressure. Moving air is known as wind.
Biosphere – The Domain of Life
• The biosphere is the narrow zone of contact between the land, water and air. It is in this zone that life, that is unique to this planet, exists. There are several species of organisms that vary in size from microbes and bacteria to huge mammals. All the living organisms including humans are linked to each other and to the biosphere for survival. The organisms in the biosphere may broadly be divided into the plant kingdom and the animal kingdom. The three domains of the earth interact with each other and affect each other in some way or the other. For example, cutting of forests for fulfilling our needs of wood, or clearing land for agriculture may lead to fast removal of soil from slopes. Similarly earth’s surface may be changed due to natural calamities like earthquakes. For example, there could be submergence of land, as happened in the case of Tsunami recently.
Parts of Andaman & Nicobar Islands were submerged under water. Discharge of waste material into lakes and rivers makes the water unsuitable for human use. It also damages other forms of life. Emission from industries, thermal power plants and vehicles, pollute the air. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is an important constituent of air. But increase in the amount of CO2 leads to increase in global temperatures. This is termed as global warming. There is thus, a need to limit the use of resources of the earth to maintain the balance of nature between the domains of the lithosphere, the atmosphere and the hydrosphere.
Evolution of The Earth
• The earth was mostly in a volatile state during its primordial stage. Due to gradual increase in density the temperature inside has increased. As a result the material inside started getting separated depending on their densities.
• This allowed heavier materials (like iron) to sink towards the centre of the earth and the lighter ones to move towards the surface. With passage of time it cooled further and solidified and condensed into a smaller size. This later led to the development of the outer surface in the form of a crust.
Evolution of Atmosphere and Hydrosphere
• There are three stages in the evolution of the present atmosphere. The first stage is marked by the loss of primordial atmosphere. In the second stage, the hot interior of the earth contributed to the evolution of the atmosphere.
• Finally, the composition of the atmosphere was modified by the living world through the process of photosynthesis. The early atmosphere, with hydrogen and helium, is supposed to have been stripped off as a result of the solar winds. This happened not only in case of the earth, but also in all the terrestrial planets.
• During the cooling of the earth, gases and water vapour were released from the interior solid earth. This started the evolution of the present atmosphere. The early atmosphere largely contained water vapour, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, methane, ammonia and very little of free oxygen. The process through which the gases were outpoured from the interior is called degassing. Continuous volcanic eruptions contributed water vapour and gases to the atmosphere.
• As the earth cooled, the water vapour released started getting condensed. The carbon dioxide in the atmosphere got dissolved in rainwater and the temperature further decreased causing more condensation and more rains. The rainwater falling onto the surface got collected in the depressions to give rise to oceans.